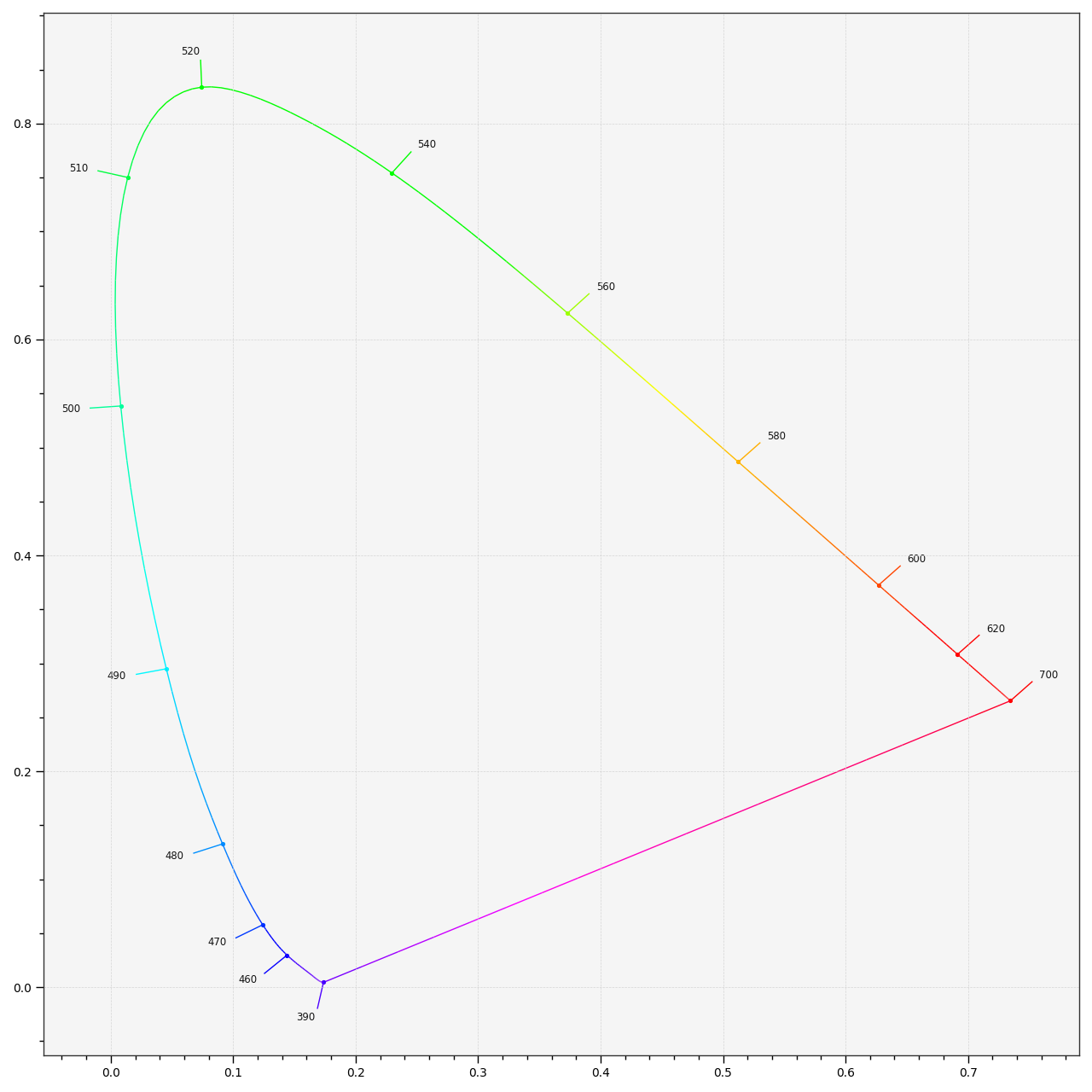
colour.plotting.diagrams.plot_spectral_locus¶
- colour.plotting.diagrams.plot_spectral_locus(cmfs: Union[MultiSpectralDistributions, str, Sequence[Union[MultiSpectralDistributions, str]]] = 'CIE 1931 2 Degree Standard Observer', spectral_locus_colours: Optional[Union[ArrayLike, str]] = None, spectral_locus_opacity: Floating = 1, spectral_locus_labels: Optional[Sequence] = None, method: Union[Literal['CIE 1931', 'CIE 1960 UCS', 'CIE 1976 UCS'], str] = 'CIE 1931', **kwargs: Any) Tuple[plt.Figure, plt.Axes][source]¶
Plot the Spectral Locus according to given method.
- Parameters
cmfs (Union[MultiSpectralDistributions, str, Sequence[Union[MultiSpectralDistributions, str]]]) – Standard observer colour matching functions used for computing the spectral locus boundaries.
cmfscan be of any type or form supported by thecolour.plotting.filter_cmfs()definition.spectral_locus_colours (Optional[Union[ArrayLike, str]]) – Colours of the Spectral Locus, if
spectral_locus_coloursis set to RGB, the colours will be computed according to the corresponding chromaticity coordinates.spectral_locus_opacity (Floating) – Opacity of the Spectral Locus.
spectral_locus_labels (Optional[Sequence]) – Array of wavelength labels used to customise which labels will be drawn around the spectral locus. Passing an empty array will result in no wavelength labels being drawn.
method (Union[Literal[('CIE 1931', 'CIE 1960 UCS', 'CIE 1976 UCS')], str]) – Chromaticity Diagram method.
kwargs (Any) – {
colour.plotting.artist(),colour.plotting.render()}, See the documentation of the previously listed definitions.
- Returns
Current figure and axes.
- Return type
Examples
>>> plot_spectral_locus(spectral_locus_colours='RGB') (<Figure size ... with 1 Axes>, <...AxesSubplot...>)